Unlike time(1) though, it will not wait until the end of a run to report the CPU usage, it continuously reports the usage in a form fit for consumption by gnuplot. In addition, it can act as a server for a GKrellm client so the data can be viewed instantaneously in a nice GUI.
Definition in file rktimes.c.
Include dependency graph for rktimes.c:

Go to the source code of this file.
Defines | |
| #define | SAMPLES_PER_SECOND 1 |
| Number of times per second to record CPU usage samples. | |
| #define | MAX_CLIENTS 8 |
| Maximum number of gkrellm clients. | |
| #define | CLIENT_BUFFER_MAX 4096 |
| Size of the buffer used to format gkrellm output. | |
| #define | __XSTRING(x) __STRING(x) |
| Convert a macro argument to a string. | |
| #define | my_perror(x) perror(x ", file " __FILE__ ", line " __XSTRING(__LINE__)) |
| A version of perror(3) that prints out the file and line number. | |
| #define | MAX_PROC_LIST 128 |
| Maximum number of processes to query in the resource set. | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | { RKTB_DONE, RKTB_CREATED_RESOURCE_SET } |
| enum | { RKTF_DONE = (1L << RKTB_DONE), RKTF_CREATED_RESOURCE_SET = (1L << RKTB_CREATED_RESOURCE_SET) } |
| enum | { RKTB_CLIENT_INITIALIZED } |
| enum | { RKTF_CLIENT_INITIALIZED = (1L << RKTB_CLIENT_INITIALIZED) } |
Functions | |
| void | rktClientWrite (unsigned int index, const char *buffer, size_t len) |
| Write a byte array to a client's socket. | |
| void | sigpass (int sig) |
| A signal handler that passes the received signal on to the child process. | |
| void | sigalrm (int sig) |
| The SIGALRM signal handler. | |
| void | sigchld (int sig) |
| Handle a SIGCHLD signal. | |
| void | sigexit (int sig) |
| Handle a SIGINT/SIGTERM signal when no utility is being monitored. | |
| void | sigio (int sig) |
| Handle a SIGIO signal. | |
| rk_resource_set_t | rktCreateSelfResourceSet (char *name) |
| Create a resource set and CPU reserve for ourself. | |
| rk_resource_set_t | rktGetChildResourceSet (rk_resource_set_t rs, const char *requested_name, const char *default_name, unsigned int child_period, unsigned int child_compute) |
| Get a resource set for the child process. | |
| void | rktUsage (FILE *file, char *prog_name) |
| Print out the usage statement to a file handle. | |
| int | rktProcessOptions (int *argc_inout, char **argv_inout[]) |
| Process the command line options. | |
| int | rktParentPart (rk_resource_set_t rs) |
| The parent portion of the fork(2) between rktimes and the monitored utility. | |
| int | rktChildPart (rk_resource_set_t rs, char *argv[]) |
| The child portion of the fork(2) between rktimes and the monitored utility. | |
| int | main (int argc, char *argv[]) |
Variables | |
| struct { | |
| unsigned long rkt_Flags | |
| const char * rkt_UtilityName | |
| timeval rkt_StartTime | |
| const char * rkt_OutputBase | |
| const char * rkt_Name | |
| unsigned int rkt_ChildPeriod | |
| unsigned int rkt_ChildCompute | |
| rk_resource_set_t rkt_ResourceSet | |
| pid_t rkt_ChildPID | |
| int rkt_ServerSocket | |
| char rkt_ClientBuffer [CLIENT_BUFFER_MAX] | |
| int rkt_ClientSockets [MAX_CLIENTS] | |
| unsigned long rkt_ClientFlags [MAX_CLIENTS] | |
| } | rktimes_data |
|
|
Convert a macro argument to a string.
|
|
|
A version of perror(3) that prints out the file and line number.
Definition at line 81 of file rktimes.c. Referenced by rktChildPart(), rktCreateSelfResourceSet(), rktGetChildResourceSet(), rktParentPart(), rktProcessOptions(), sigalrm(), and sigpass(). |
|
||||||||||||
|
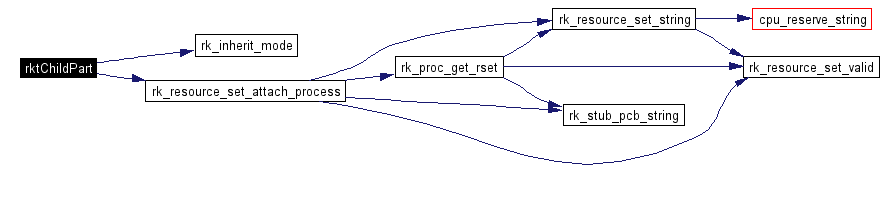
The child portion of the fork(2) between rktimes and the monitored utility. This function will attach the child to the given resource set and execvp(3) the utility to monitor with the given arguments.
Definition at line 1072 of file rktimes.c. References ensure, my_perror, NULL_RESOURCE_SET, require, rk_inherit_mode(), rk_resource_set_attach_process(), and rk_resource_set_t. |
Here is the call graph for this function:
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Write a byte array to a client's socket. If they happen to fall behind or some other error is encountered, the socket is closed immediately and erased from the rktimes_data.rkt_ClientSockets array.
Definition at line 158 of file rktimes.c. References MAX_CLIENTS, and require. |
|
|
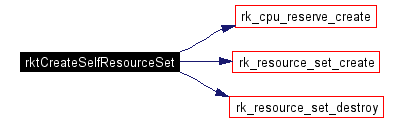
Create a resource set and CPU reserve for ourself. Otherwise, we might not get CPU time to do the recording.
Definition at line 431 of file rktimes.c. References my_perror, NULL_RESOURCE_SET, require, RK_ANY_CPU, rk_cpu_reserve_create(), RK_NAME_LEN, rk_reserve_t, rk_resource_set_create(), rk_resource_set_destroy(), rk_resource_set_t, and RSV_SOFT. |
Here is the call graph for this function:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
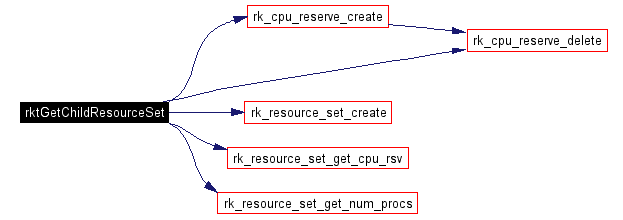
Get a resource set for the child process. If a resource set already exists with the requested name, that will be used. Otherwise, a new one will be created. If no name is requested, a new set will be created with the default name.
Definition at line 494 of file rktimes.c. References cpu_reserve_attr::blocking_time, cpu_reserve_attr::compute_time, cpu_reserve_attr::deadline, rk_reserve_param::enf_mode, my_perror, NULL_RESERVE, NULL_RESOURCE_SET, cpu_reserve_attr::period, cpu_reserve_attr::processor, rk_reserve_param::rep_mode, require, cpu_reserve_attr::reserve_type, RK_ANY_CPU, rk_cpu_reserve_create(), rk_cpu_reserve_delete(), RK_NAME_LEN, rk_reserve_t, rk_resource_set_create(), rk_resource_set_get_cpu_rsv(), rk_resource_set_get_num_procs(), rk_resource_set_t, RSV_SOFT, rk_reserve_param::sch_mode, and cpu_reserve_attr::start_time. |
Here is the call graph for this function:
|
|
The parent portion of the fork(2) between rktimes and the monitored utility. This function will attach itself to a resource set to ensure that it has some CPU time to work and then wait for gkrellm connections or the child's death.
Definition at line 885 of file rktimes.c. References ensure, my_perror, NULL_RESOURCE_SET, require, rk_resource_set_attach_process(), rk_resource_set_t, SAMPLES_PER_SECOND, sigalrm(), sigchld(), sigexit(), sigio(), and sigpass(). |
Here is the call graph for this function:
|
||||||||||||
|
Process the command line options.
Definition at line 644 of file rktimes.c. References my_perror, NULL_RESOURCE_SET, require, RK_NAME_LEN, rk_resource_set_get_by_name(), string_to_microsec(), and us_time. |
Here is the call graph for this function:

|
||||||||||||
|
Print out the usage statement to a file handle.
Definition at line 594 of file rktimes.c. References require. |
|
|
The SIGALRM signal handler. This function will be called SAMPLES_PER_SECOND times a second to read the CPU usage of the resource set's processes. The data is then output to a file and echoed to any gkrellm clients.
Definition at line 212 of file rktimes.c. References CLIENT_BUFFER_MAX, cpu_reserve_attr::compute_time, cpCreateChildProcess(), cpFindChildProcess(), cpOpenOutput(), cpSampleUsage(), cpu_reserve_attr::deadline, GKA_CPUIdle, GKA_CPUReserveIdle, GKA_CPUReserveNice, GKA_CPUReserveUser, GKA_CPUUser, GKA_Processes, GKA_ProcessesRunning, GKA_TAG_DONE, GKA_UpTime, gkFormatUpdate(), gkInitialUpdateClose, gkInitialUpdateOpen, MAX_CLIENTS, MAX_PROC_LIST, my_perror, NULL_RESERVE, cpu_reserve_attr::period, require, rk_cpu_reserve_get_attr(), rk_reserve_t, rk_resource_set_get_cpu_rsv(), rk_resource_set_get_proclist(), rktClientWrite(), and SAMPLES_PER_SECOND. Referenced by rktParentPart(). |
Here is the call graph for this function:
|
|
Handle a SIGCHLD signal. This function will be called when the child exits.
Definition at line 347 of file rktimes.c. References require. Referenced by rktParentPart(). |
|
|
Handle a SIGINT/SIGTERM signal when no utility is being monitored.
Definition at line 360 of file rktimes.c. References require. Referenced by rktParentPart(). |
|
|
Handle a SIGIO signal. This function will be called when the server socket has a new connection waiting to be accept(2)'d.
Definition at line 373 of file rktimes.c. References CLIENT_BUFFER_MAX, GKA_HostName, GKA_SystemName, GKA_TAG_DONE, gkFormatPreamble(), MAX_CLIENTS, require, and rktClientWrite(). Referenced by rktParentPart(). |
Here is the call graph for this function:
|
|
A signal handler that passes the received signal on to the child process.
Definition at line 188 of file rktimes.c. References my_perror, and require. Referenced by rktParentPart(). |
 1.3.6
1.3.6